Most recent
ASTM E350-23
Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Carbon Steel, Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and Wrought Iron
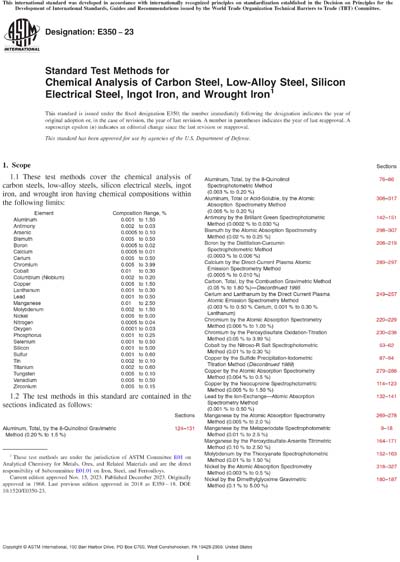
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of carbon steels, low-alloy steels, silicon electrical steels, ingot iron, and wrought iron having chemical compositions within the following limits:
| Element | Composition Range, % |
| Aluminum | 0.001 to 1.50 |
| Antimony | 0.002 to 0.03 |
| Arsenic | 0.0005 to 0.10 |
| Bismuth | 0.005 to 0.50 |
| Boron | 0.0005 to 0.02 |
| Calcium | 0.0005 to 0.01 |
| Cerium | 0.005 to 0.50 |
| Chromium | 0.005 to 3.99 |
| Cobalt | 0.01 to 0.30 |
| Columbium (Niobium) | 0.002 to 0.20 |
| Copper | 0.005 to 1.50 |
| Lanthanum | 0.001 to 0.30 |
| Lead | 0.001 to 0.50 |
| Manganese | 0.01 to 2.50 |
| Molybdenum | 0.002 to 1.50 |
| Nickel | 0.005 to 5.00 |
| Nitrogen | 0.0005 to 0.04 |
| Oxygen | 0.0001 to 0.03 |
| Phosphorus | 0.001 to 0.25 |
| Selenium | 0.001 to 0.50 |
| Silicon | 0.001 to 5.00 |
| Sulfur | 0.001 to 0.60 |
| Tin | 0.002 to 0.10 |
| Titanium | 0.002 to 0.60 |
| Tungsten | 0.005 to 0.10 |
| Vanadium | 0.005 to 0.50 |
| Zirconium | 0.005 to 0.15 |
1.2 The test methods in this standard are contained in the sections indicated as follows:
|
| Sections |
|
|
|
| Aluminum, Total, by the 8-Quinolinol Gravimetric | 124–131 |
| Aluminum, Total, by the 8-Quinolinol | 76–86 |
| Aluminum, Total or Acid-Soluble, by the Atomic | 308–317 |
| Antimony by the Brilliant Green Spectrophotometric | 142–151 |
| Bismuth by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 298–307 |
| Boron by the Distillation-Curcumin | 208–219 |
| Calcium by the Direct-Current Plasma Atomic | 289–297 |
| Carbon, Total, by the Combustion Gravimetric Method |
|
| Cerium and Lanthanum by the Direct Current Plasma | 249–257 |
| Chromium by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 220–229 |
| Chromium by the Peroxydisulfate Oxidation-Titration | 230–238 |
| Cobalt by the Nitroso-R Salt Spectrophotometric | 53–62 |
| Copper by the Sulfide Precipitation-Iodometric | 87–94 |
| Copper by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 279–288 |
| Copper by the Neocuproine Spectrophotometric | 114–123 |
| Lead by the Ion-Exchange—Atomic Absorption | 132–141 |
| Manganese by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 269–278 |
| Manganese by the Metaperiodate Spectrophotometric | 9–18 |
| Manganese by the Peroxydisulfate-Arsenite Titrimetric | 164–171 |
| Molybdenum by the Thiocyanate Spectrophotometric | 152–163 |
| Nickel by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 318–327 |
| Nickel by the Dimethylglyoxime Gravimetric | 180–187 |
| Nickel by the Ion-Exchange-Atomic-Absorption | 188–197 |
| Nitrogen by the Distillation-Spectrophotometric | 63–75 |
| Phosphorus by the Alkalimetric Method | 172–179 |
| Phosphorus by the Molybdenum Blue | 19–30 |
| Silicon by the Molybdenum Blue Spectrophotometric | 103–113 |
| Silicon by the Gravimetric Titration | 46–52 |
| Sulfur by the Gravimetric Method | 31–36 |
| Sulfur by the Combustion-Iodate Titration Method | 37–45 |
| Tin by the Sulfide Precipitation-Iodometric Titration | 95–102 |
| Tin by the Solvent Extraction-Atomic Absorption | 198–207 |
| Titanium by the Diantipyrylmethane | 258–268 |
| Vanadium by the Atomic Absorption Spectrometry | 239–248 |
1.3 Test methods for the determination of several elements not included in this standard can be found in Test Methods E1019.
1.4 Some of the composition ranges given in 1.1 are too broad to be covered by a single test method and therefore this standard contains multiple test methods for some elements. The user must select the proper test method by matching the information given in the Scope and Interference sections of each test method with the composition of the alloy to be analyzed.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. In some cases, exceptions allowed in IEEE/ASTM SI 10 are also used.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 6 and in special “Warning” paragraphs throughout these test methods.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ASTM International [astm]